- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
AQA A Level Physics復習筆記3.5.2 Snell's Law
Snell's Law
- Snell’s law relates the angle of incidence to the angle of refraction, it is given by:
n1?sin?θ1?=?n2?sin?θ2
- Where:
- n1?= the refractive index of material 1
- n2?= the refractive index of material 2
- θ1?= the angle of incidence of the ray in material 1
- θ2?= the angle of refraction of the ray in material 2
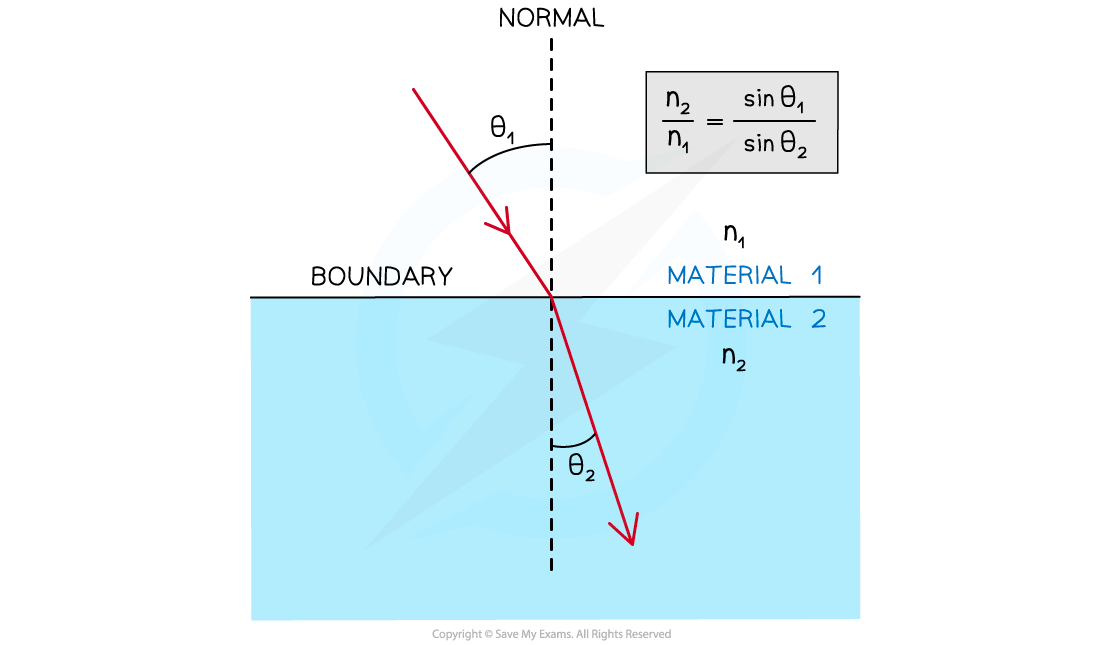
- θ1?and?θ2?are always taken from the?normal
- Material 1 is always the material in which the ray goes through?first
- Material 2 is always the material in which the ray goes through?second
Worked Example
A light ray is directed at a vertical face of a glass cube. The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram.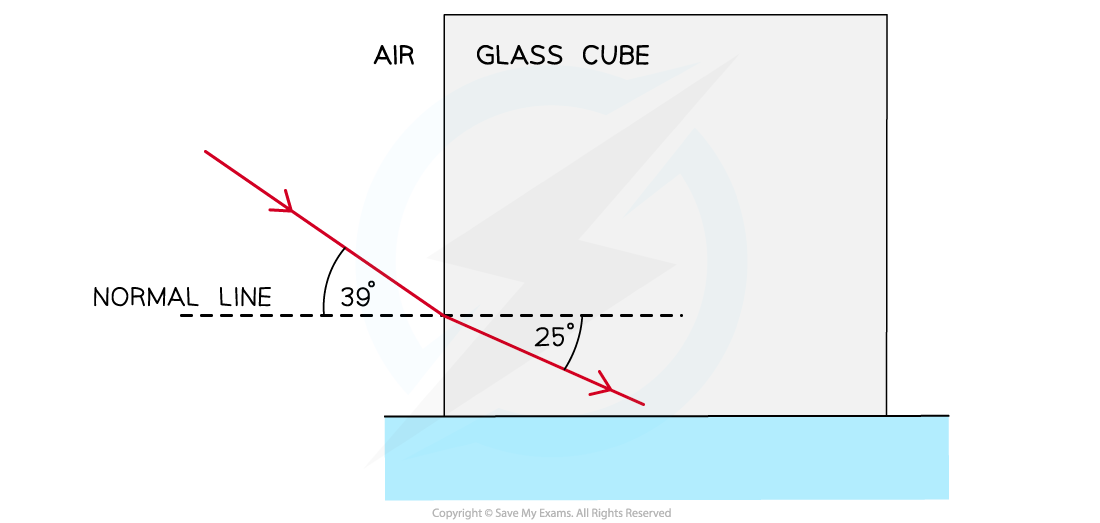 Show that the refractive index of the glass is about 1.5.
Show that the refractive index of the glass is about 1.5.


Exam Tip
Always check that the angle of incidence and refraction are the angles between the normal and the light ray. If the angle between the light ray and the boundary is calculated instead, calculate 90 – θ (since the normal is perpendicular to the boundary) to get the correct angle
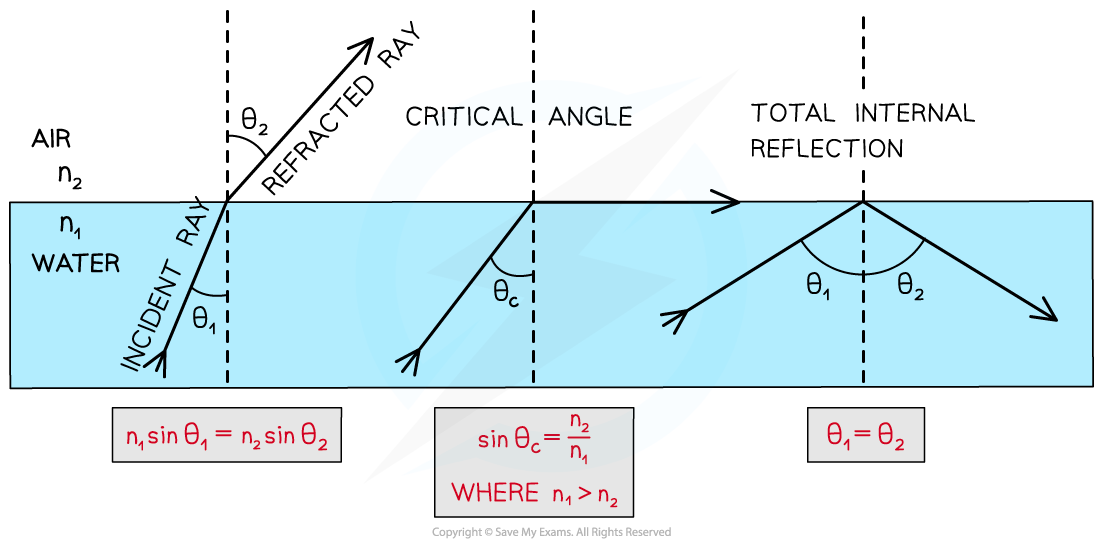
Total Internal Reflection
- As the angle of incidence is increased, the angle of refraction also increases until it gets closer to 90°
- When the angle of refraction is exactly 90° the light is refracted along the boundary
- At this point, the angle of incidence is known as the?critical angle?θc
- This angle can be found using the formula:
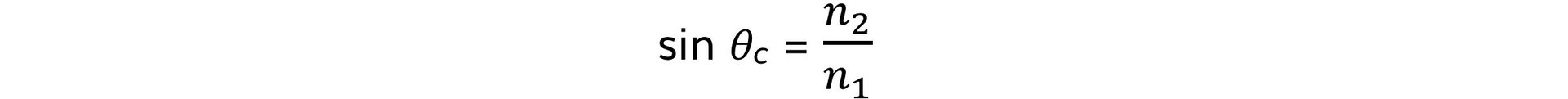
- This can easily be derived from Snell’s law where:
- θ1?=?θc
- θ2?= 90°
- n1?>?n2
- Total internal reflection (TIR) occurs when:
The angle of incidence is greater than the critical angle and the incident refractive index n1?is greater than the refractive index of the material at the boundary n2
- Therefore, the?two?conditions for total internal reflection are:
- The angle of incidence > the critical angle
- The refractive index?n1?is greater than the refractive index?n2
Worked Example
A glass cube is held in contact with a liquid and a light ray is directed at a vertical face of the cube.The angle of incidence at the vertical face is 39° and the angle of refraction is 25° as shown in the diagram.The light ray is totally internally reflected at?X.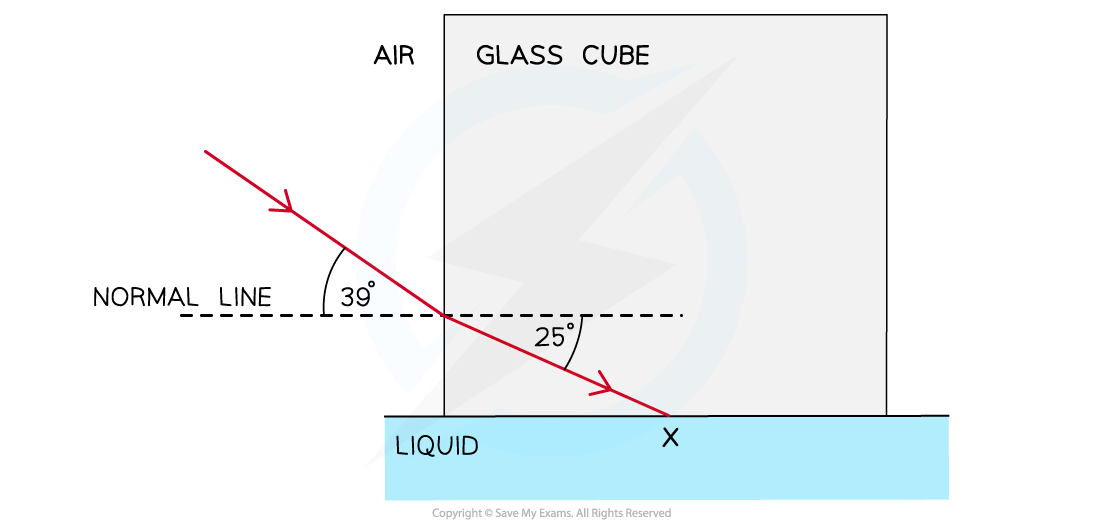 (i) Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond?X?to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.(ii) Calculate the refractive index of the liquid.
(i) Complete the diagram to show the path of the ray beyond?X?to the air and calculate the critical angle for the glass-liquid boundary.(ii) Calculate the refractive index of the liquid.
(i)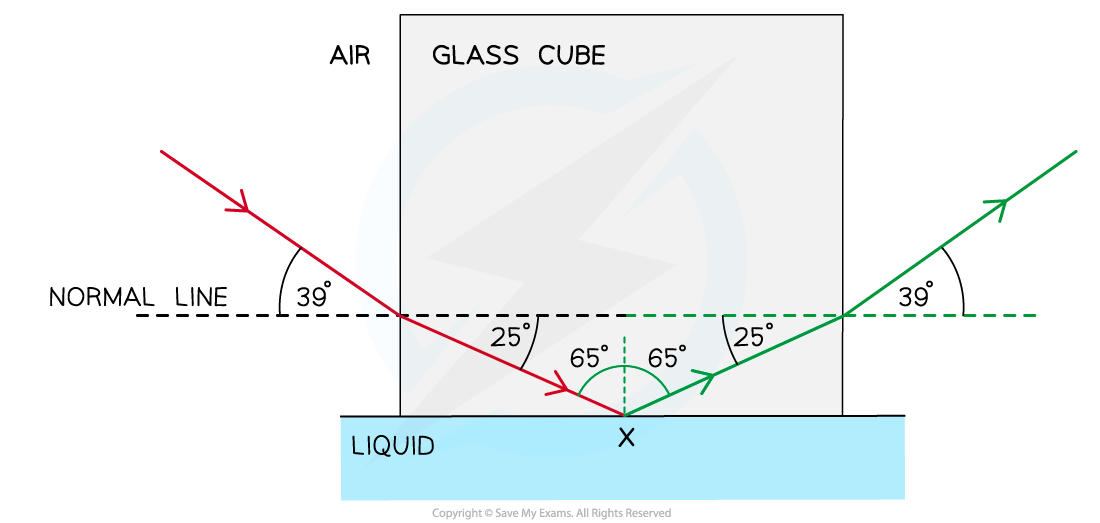 Step 1: Draw the reflected angle at the glass-liquid boundary
Step 1: Draw the reflected angle at the glass-liquid boundary
- When a light ray is reflected, the angle of incidence = angle of reflection
- Therefore, the angle of incidence (or reflection) is 90° – 25° = 65°
Step 2: Draw the refracted angle at the glass-air boundary
- At the glass-air boundary, the light ray refracts?away?from the normal
- Due to the reflection, the light rays are symmetrical to the other side
Step 3: Calculate the critical angle
- The question states the ray is “totally internally reflected for the first time” meaning that this is the lowest angle at which TIR occurs
- Therefore, 65° is the critical angle
(ii)Step 1: Write down the known quantities
- Refractive index of glass,?n1?= 1.489 (from previous worked example)
- Refractive index of liquid =?n2
- Angle of incidence / critical angle,?θ1?=?θc?= 65°
- Angle of refraction,?θ2?= 90°
Step 2: Write out Snell’s Law or the equation for critical angle
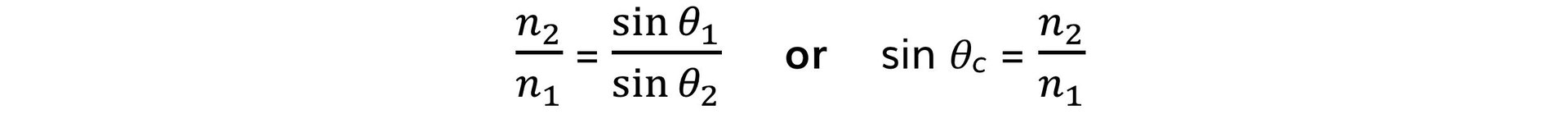
Step 3: Calculate the refractive index of the liquid

轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









