- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Physics 復習筆記 5.3.5 The Pressure Law
Edexcel IGCSE Physics 復習筆記 5.3.5 The Pressure Law
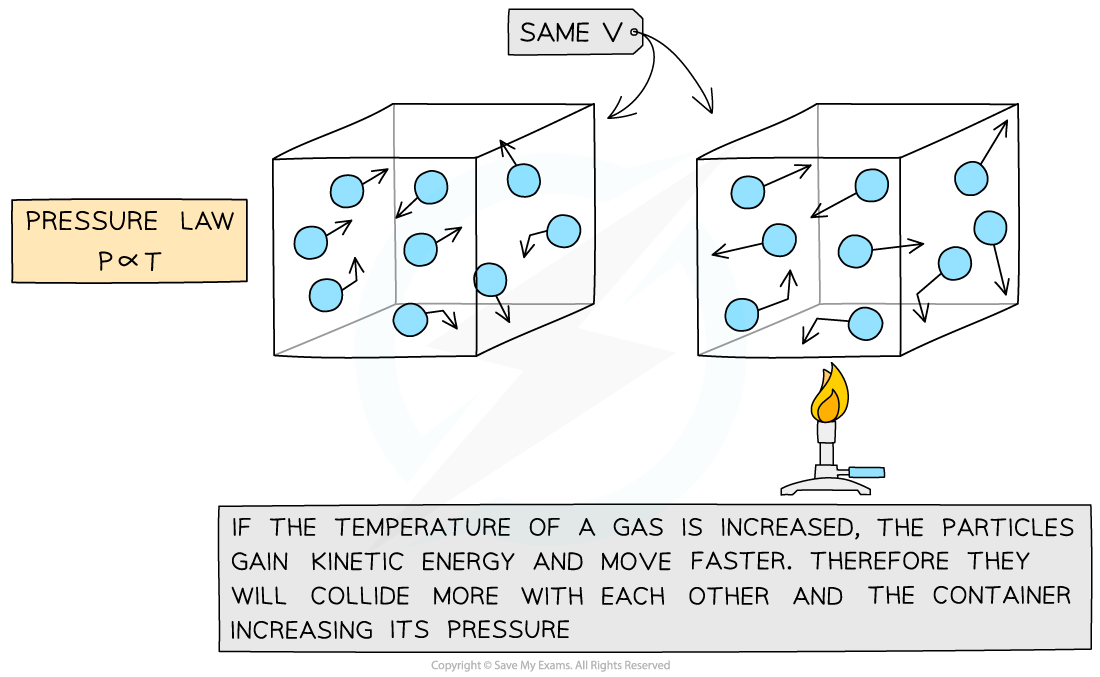
The Pressure Law
- If the volume?V?of an ideal gas is constant, the?pressure law?is given by:
P?∝?T
- This means the pressure is?proportional?to the temperature
- The relationship between the pressure and (Kelvin) temperature for a fixed mass of gas at constant volume can also be written as:
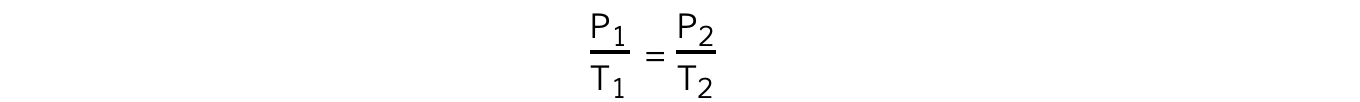
- Where:
- P1?= initial pressure (Pa)
- P2?= final pressure (Pa)
- T1?= initial temperature (K)
- T2?= final temperature (K)
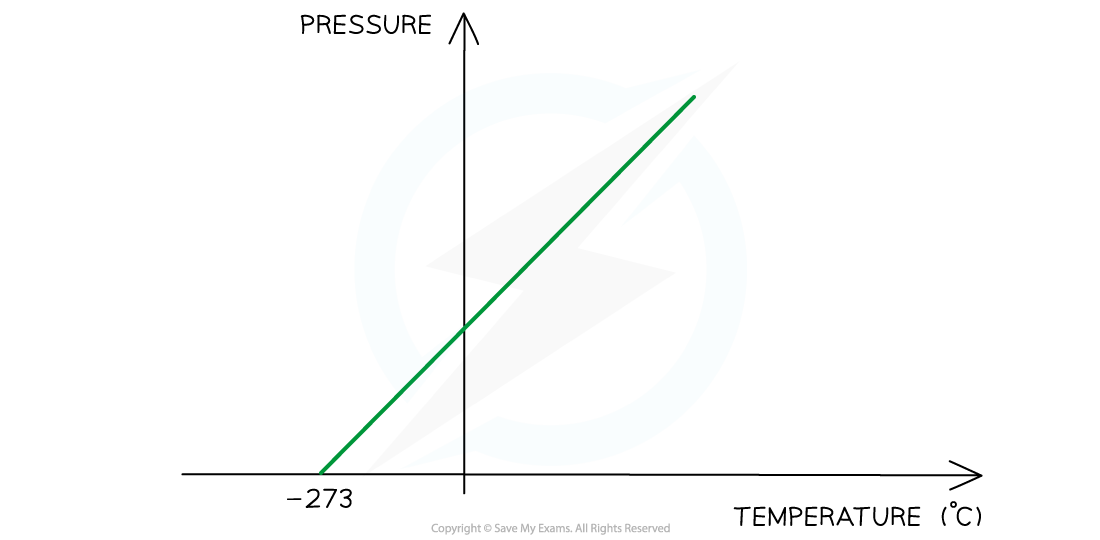
Pressure law graph representing temperature (in °C) directly proportional to the volume
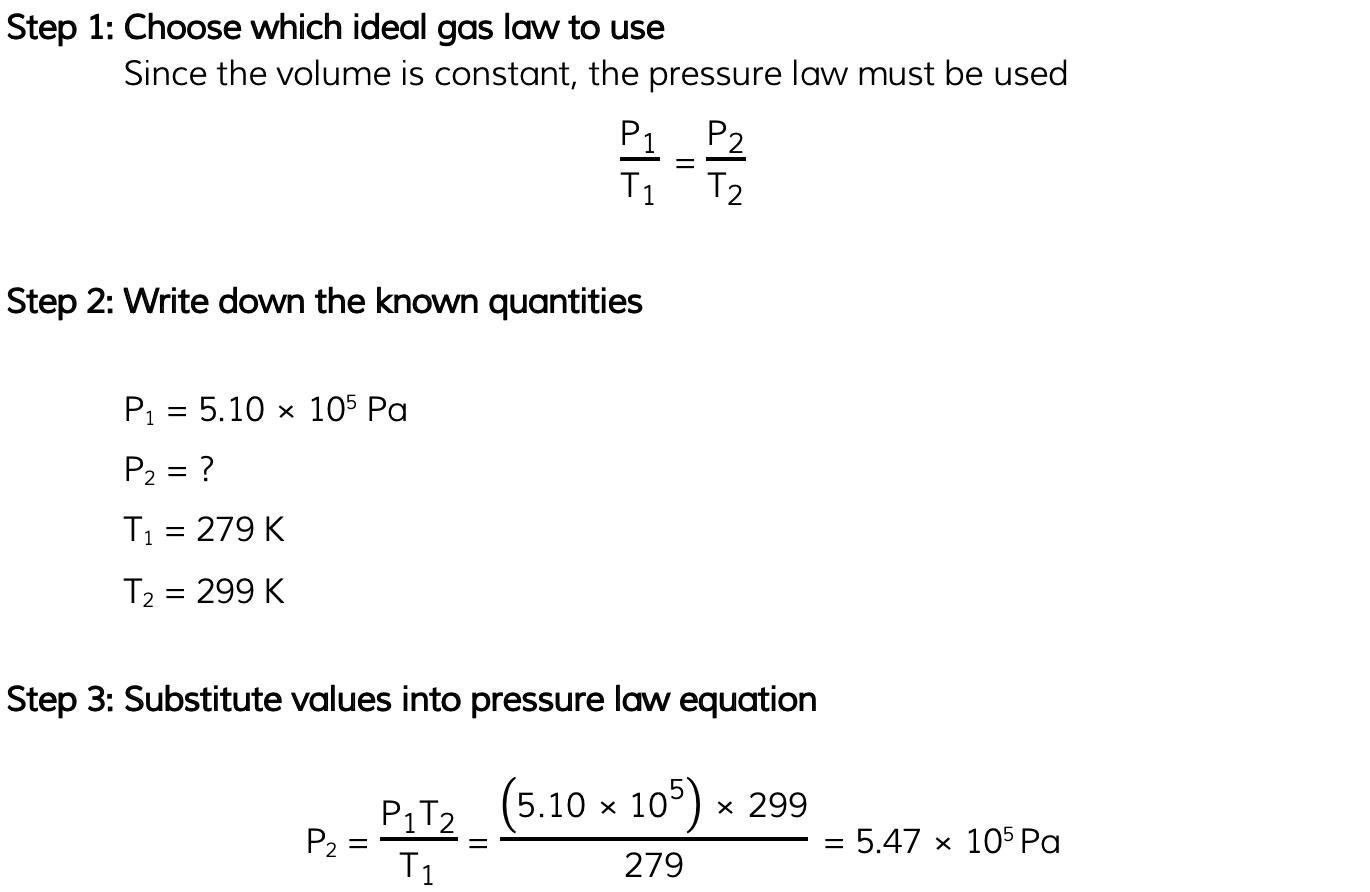
Worked Example
The pressure inside a bicycle tyre is 5.10 × 105?Pa when the temperature is 279 K. After the bicycle has been ridden, the temperature of the air in the tyre is 299 K.Calculate the new pressure in the tyre, assuming the volume is unchanged.
Exam Tip
Remember when using gas law the temperature?T?must always be in?kelvin?(K)!
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









