- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Physics 復(fù)習(xí)筆記 6.1.6 The Motor Effect
Edexcel IGCSE Physics 復(fù)習(xí)筆記 6.1.6 The Motor Effect
Magnetic Force on a Current-Carrying Wire
- The?motor effect?occurs:
When a wire with current flowing through it is placed in a magnetic field and experiences a force
- This effect is a result of?two?interacting?magnetic fields
- One is produced around the wire due to the current flowing through it
- The second is the magnetic field into which the wire is placed, for example, between two magnets
- As a result of the interactions of the two magnetic fields, the wire will experience a?force

The motor effect is a result of two magnetic fields interacting to produce a force on the wire
Simple Motors
- The?motor effect?can be used to create a simple?d.c?electric motor
- The simple d.c. motor consists of a coil of wire (which is free to rotate) positioned in a?uniform magnetic field:
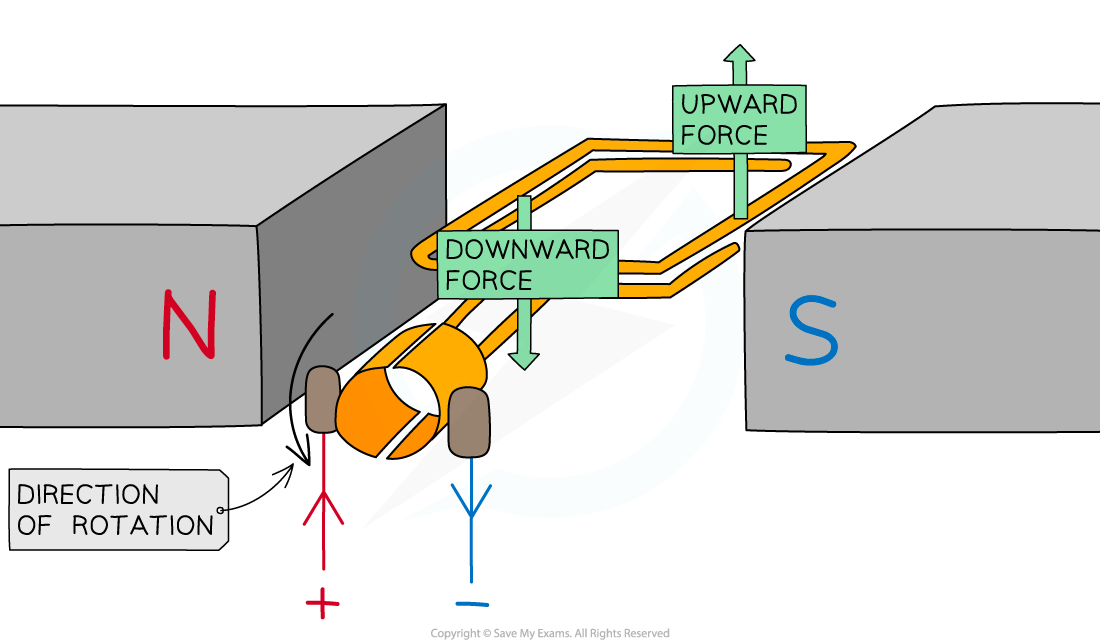
A simple d.c. motor consisting of two magnets, a coil and a split ring commutator to control the direction of the current
- When the current is flowing in the coil at 90o?to the direction of the magnetic field:
- The?current?creates a?magnetic field?around the coil
- The magnetic field produced around the coil interacts with the field produced by the magnets
- This results in a?force?being exerted on the coil
- The direction of the force can be determined using?Fleming's left-hand rule
- As current will flow in?opposite?directions on each side of the coil, the force produced from the magnetic field will push one side of the coil?up?and the other side of the coil?down
- This will cause the coil to?rotate, and it will continue to rotate until it is in the vertical position
- When the coil is in the vertical position there will be a force acting upwards and a force acting downwards
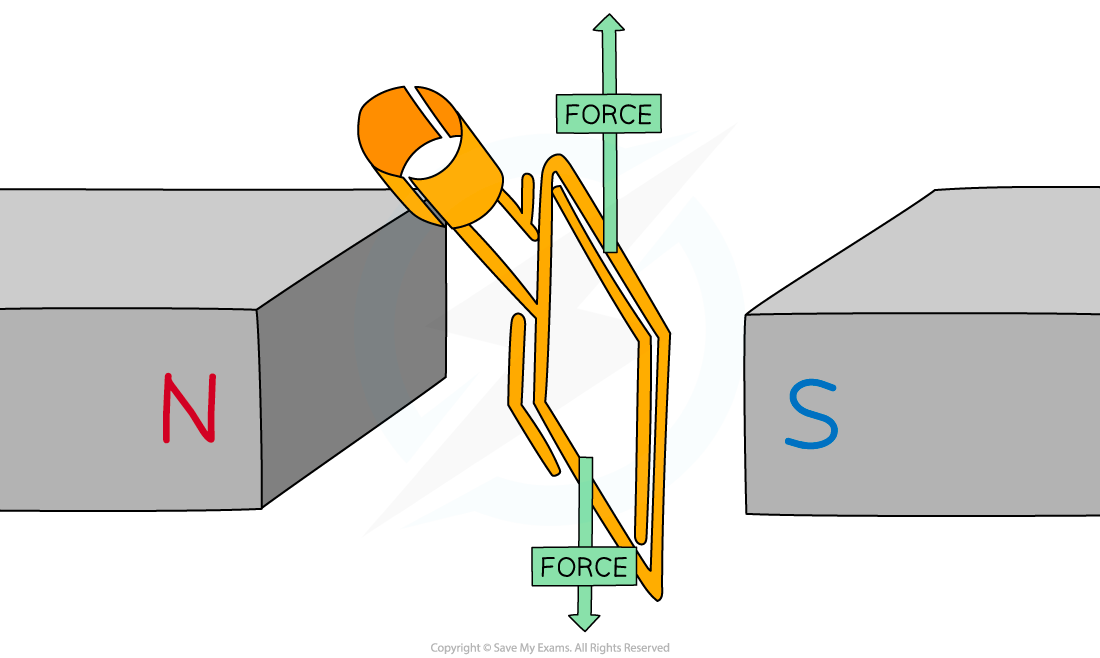
Forces acting on the coil in the vertical position
- The?split ring commutator?swaps the contacts of the coil
- This reverses the direction in which the current is flowing
- Reversing the direction of the current will also reverse the direction in which the forces are acting
- As a result, the coil will continue to?rotate
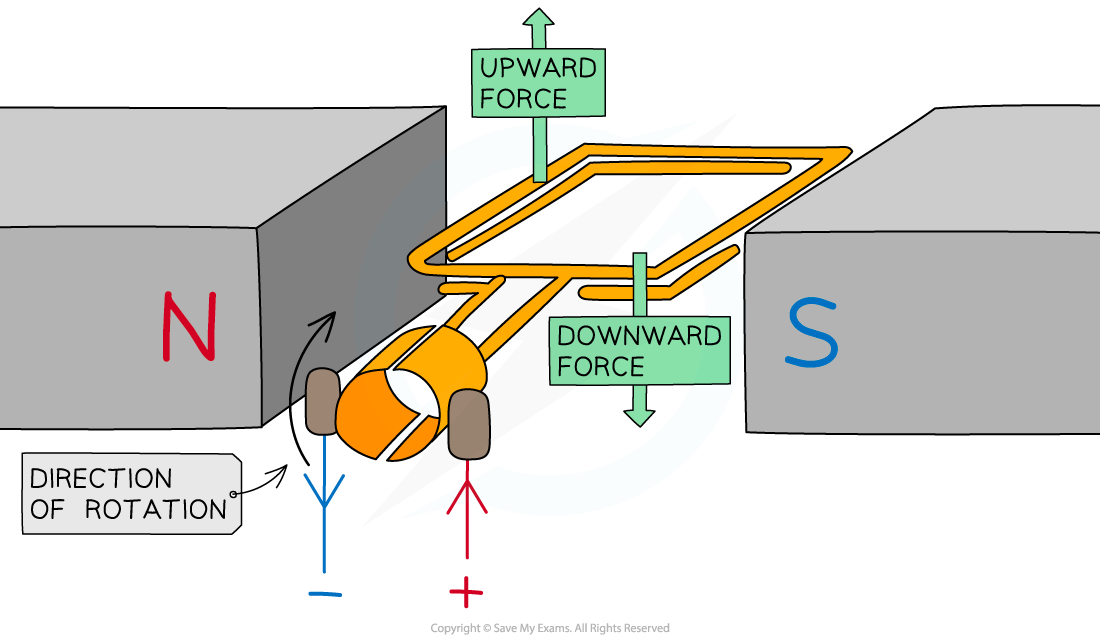
Forces on coil after commutator has reversed the direction of the current
- The commutator reverses the direction of the current in the coil every?half turn
- This will keep the coil rotating continuously as long as the current is flowing
Factors Affecting the D.C Motor
- The?speed?at which the coil rotates can be increased by:
- Increasing the?current
- Increasing the strength of the?magnetic field
- The?direction of rotation?of coil in the d.c motor can be changed by:
- Reversing the direction of the?current
- Reversing the direction of the magnetic field by reversing the?poles?of the magnet
- The?force?supplied by the motor can be increased by:
- Increasing the?current?in the coil
- Increasing the strength of the?magnetic field
- Adding?more turns?to the coil
Loudspeakers
- Loudspeakers and headphones convert electrical signals into sound
- They work due to the?motor effect
- They work in the opposite way to microphones
- A loudspeaker consists of a?coil of wire?which is wrapped around one pole of a?permanent magnet
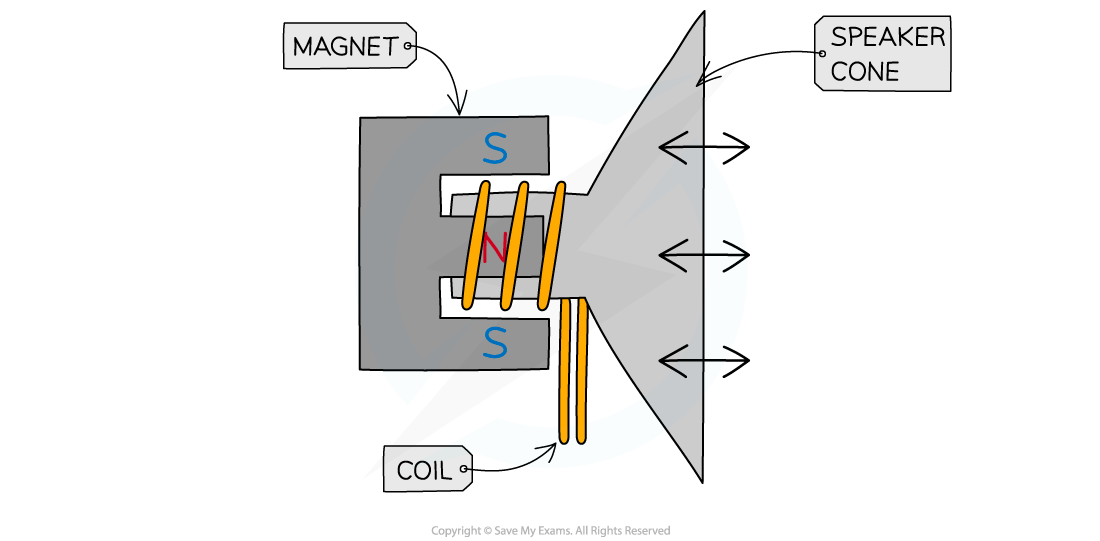
Diagram showing a cross-section of a loudspeaker
- An?alternating current?passes through the coil of the loudspeaker
- This creates a?changing magnetic field?around the coil
- As the current is constantly changing direction, the direction of the magnetic field will be?constantly changing
- The magnetic field produced around the coil?interacts?with the field from the permanent magnet
- The interacting magnetic fields will exert a?force?on the coil
- The direction of the force at any instant can be determined using?Fleming’s left-hand rule
- As the magnetic field is constantly changing direction, the?force?exerted on the coil will?constantly change direction
- This makes the coil?oscillate
- The oscillating coil causes the speaker cone to oscillate
- This makes the air oscillate, creating?sound waves
Worked Example
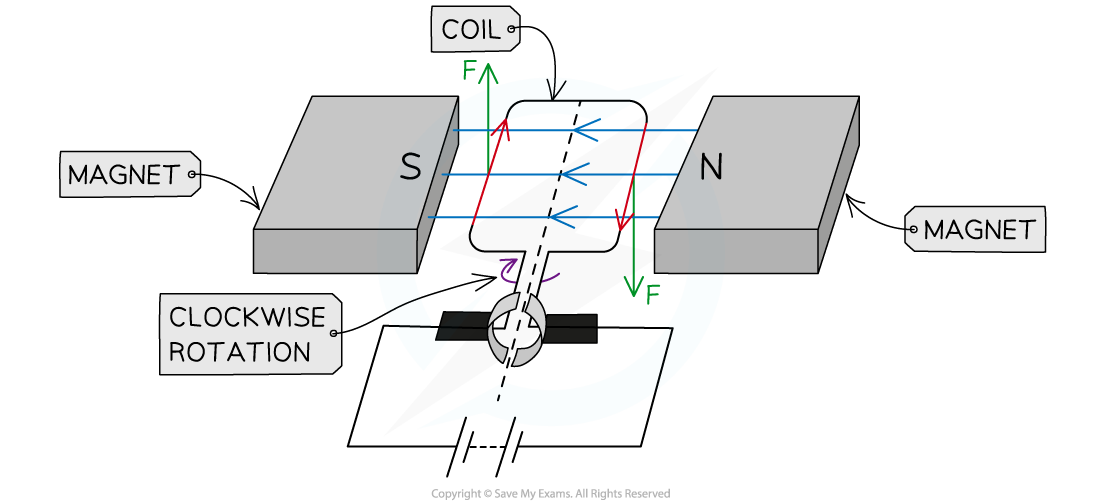
A d.c motor is set up as shown below.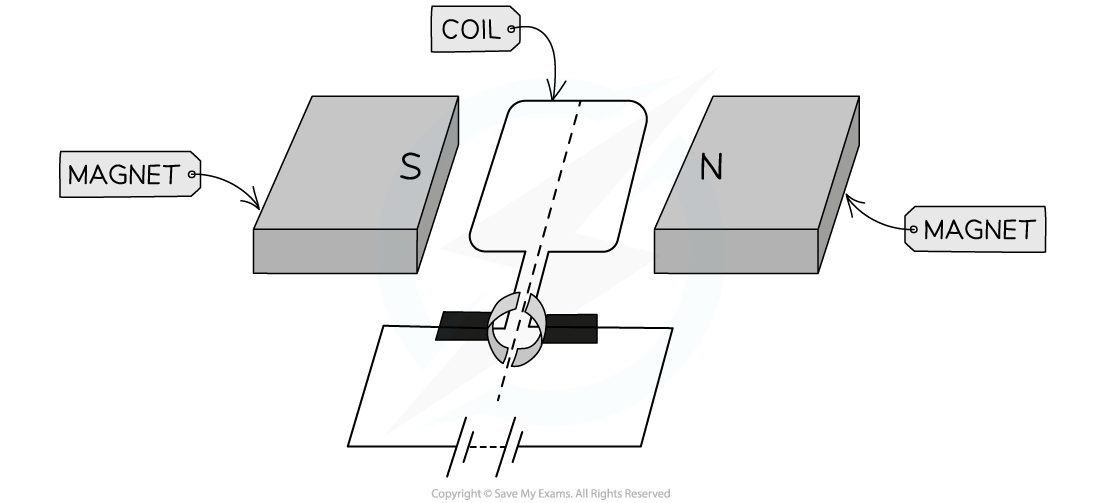 Determine whether the coil will be rotating clockwise or anticlockwise.
Determine whether the coil will be rotating clockwise or anticlockwise.
Step 1: Draw arrows to show the direction of the magnetic field lines
-
- These will go from the north pole of the magnet to the south pole of the magnet
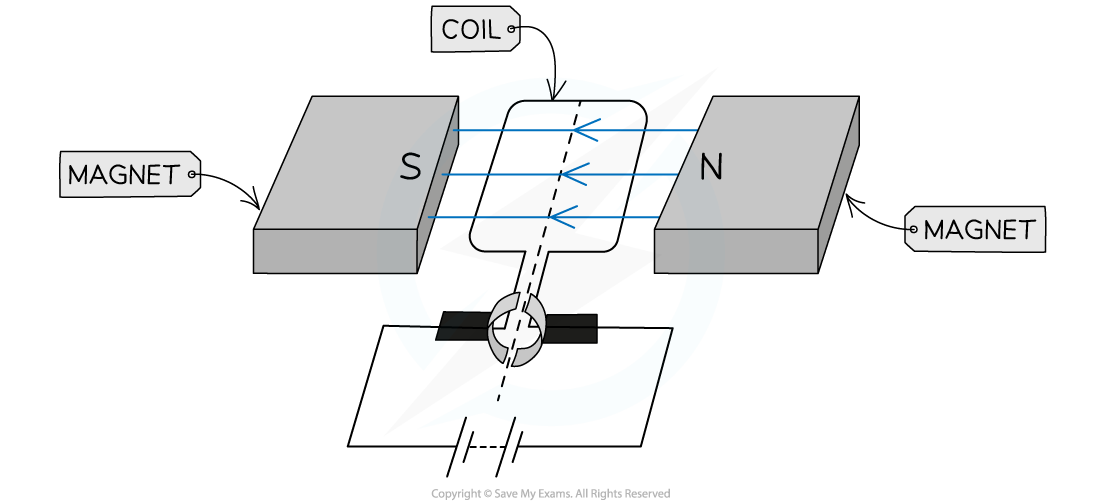
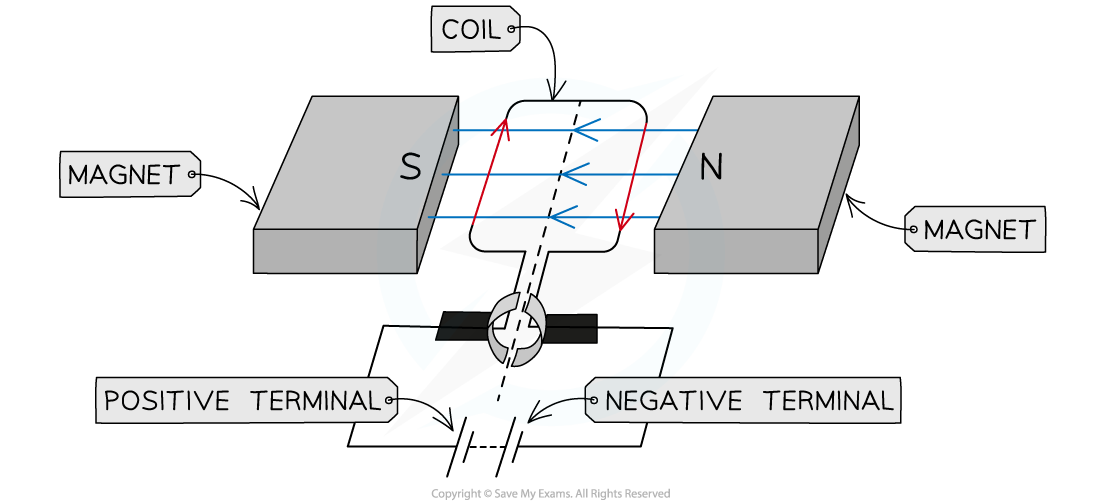
Step 2: Draw arrows to show the direction the current is flowing in the coils
-
- Current will flow from the positive terminal of the battery to the negative terminal
Step 3: Use Fleming’s left hand rule to determine the direction of the force on each side of the coil
-
- Start by pointing your?First?Finger in the direction of the (magnetic)?Field
- Now rotate your hand around the first finger so that the seCond finger points in the direction of the?Current
- The?THumb will now be pointing in the direction of the?THrust (the force)
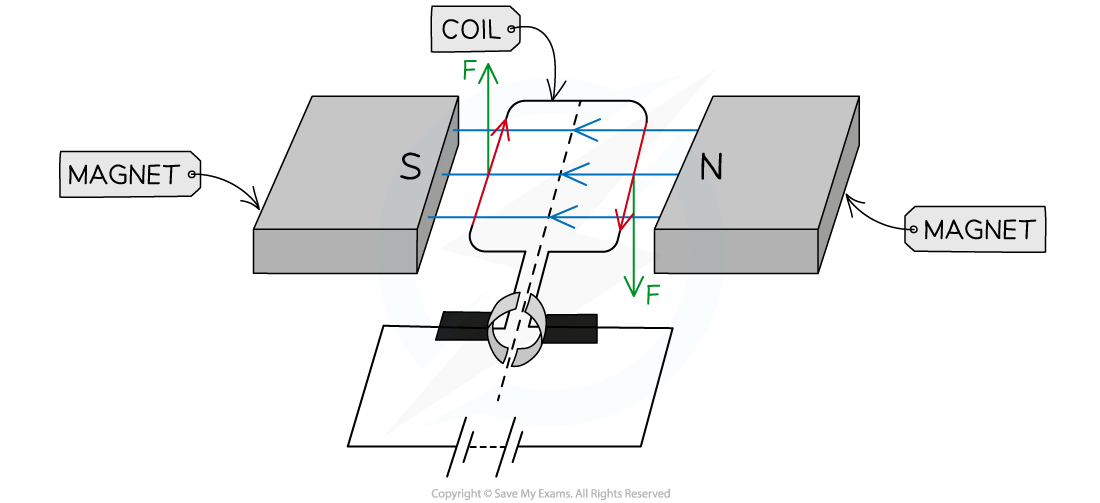
Step 4: Use the force arrows to determine the direction of rotation
-
- The coil will be turning?clockwise
Exam Tip
The explanation of the loudspeaker is very similar to the explanation of a motor, however?direct current?is used in a d.c motor and?alternating current?is used in a loudspeaker. You need to learn how both work.When explaining how a loudspeaker works remember to refer to the?alternating current?and the?changing magnetic field?that it creates.
Factors Affecting Magnetic Force
- Magnetic forces are due to interactions between?magnetic fields
- Stronger?magnetic fields produce?stronger?forces and vice versa
- For a current carrying conductor, the size of the force exerted by the magnetic fields can be?increased?by:
- Increasing the amount of?current?flowing through the wire
- This will increase the magnetic field around the wire
- Using?stronger magnets
- This will increase the magnetic field between the poles of the magnet
- Placing the wire at?90o?to the direction of the magnetic field lines between the poles of the magnet
- This will result in the maximum interaction between the two magnetic fields
- Increasing the amount of?current?flowing through the wire
- Note: If the two magnetic fields are?parallel?there will be no interaction between the two magnetic fields and therefore?no force?produced
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









