- 翰林提供學術活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學背景提升服務!
- 400 888 0080
Edexcel IGCSE Geography 復習筆記 3.2.3 Impacts of Natural Hazards
Edexcel IGCSE Geography 復習筆記 3.2.3 Impacts of Natural Hazards
Impacts of Natural Hazards
- Natural hazards are when they affect people; they have both short and long term impacts
Short & Long Term Impacts of Hazard Events
| Short Term Impacts | Long Term Impacts |
| Damage to properties from high wind, heavy rain and storm surges, power cables and telephone lines | Rebuilding of homes, schools, infrastructure and businesses can take time |
| Impact on businesses, tourism and transport | Cost of rebuilding affects the economy, increased unemployment |
| Landslides | Stricter building codes introduced |
| Deaths and injuries, decrease in quality of life | Mental health, Post Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) |
| Crops destroyed, impacting on farmers incomes and increasing food prices | Risk assessment and hazard mapping reviewed |
| Habitat destruction |
Exam Tip
In the exam you may be asked to analyse the short and long term impacts of an earthquake event. In your answer you need to consider:
- Why short and long term impacts vary - the size and magnitude of the event
- What are the main short and long term impacts
- How the impacts are affected by the level of development, location and accessibility of the area
- What are the knock-on effects of some impacts e.g. water supplies being contaminated can lead to disease
Case Study: Impacts of Tropical Cyclones
- Name - Haiyan (Yolanda)
- Location - Philippines, Vietnam and Taiwan
- Date - November 2013
- Magnitude - Category 5
- Highest wind speed - 315km/h
- Storm surge - up to 6m
- Rainfall - 282mm in 12 hours
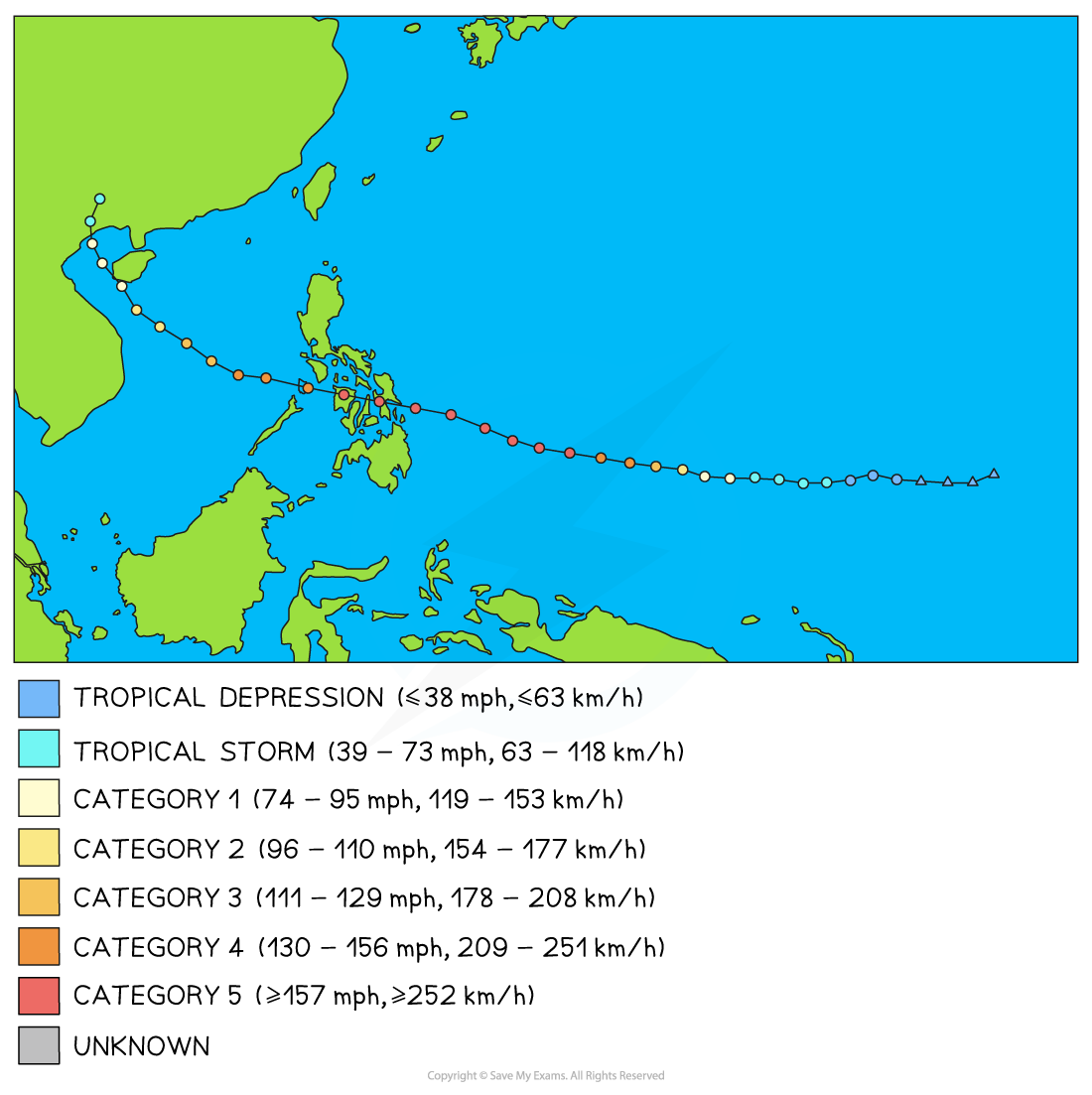 Path of Tropical Cyclone Haiyan (Yolanda)
Path of Tropical Cyclone Haiyan (Yolanda)| Short Term Impacts | Long Term Impacts |
| Estimated 6400 deaths | Cost US$5.8 billion |
| 4.1 million people made homeless | Build Back Better launched in 2014 to upgrade buildings to reduce the damage from future tropical cyclones. However, by 2016 only 1% of target of 200,000 homes had been achieved |
| 90% Tacloban destroyed | No build zone along the Eastern Visayas coastline |
| Roads blocked by debris and landslides | Storm surge warning system |
| Electricity supply down in some areas for six weeks | Mangroves replanted |
| Airport at Tacloban badly damaged | Tropical storm shelters built inland |
| 1.1 million tonnes of crops destroyed | One year on 4 million people still in temporary shelters |
| 33 million coconut trees destroyed | Six months after in Tacloban access to clean water was still limited |
| 1.1 million homes damaged or destroyed | |
| 14 million people affected | |
| Landslides |
Case Study: Impacts of Earthquakes
- Name - Gorkha
- Location - Nepal
- Date - 25th April 2015
- Epicentre - Barpak village, 60km north-west of Kathmandu (capital)
- Depth - 15km
- Magnitude - 7.8
- Plate boundary - Collision plate where Indian plate collides with the Eurasian plate
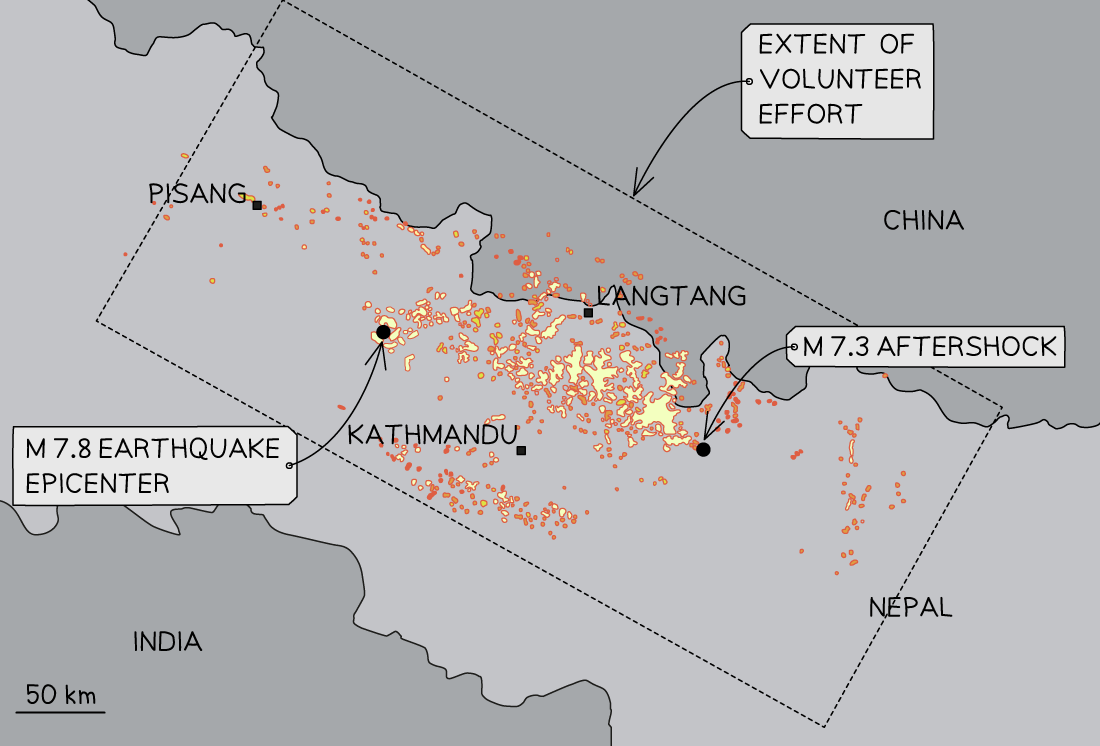 Landslides triggered by the Gorkha earthquake
Landslides triggered by the Gorkha earthquake| Short Term Impacts | Longer Term Impacts |
| Approximately 8600 deaths | Cost US$10 billion |
| 19,000 injuries | 7000 schools rebuilt |
| Avalanches on Mount Everest and in the Langtang valley | Two years later 70% of displaced people still in temporary shelters |
| Roads blocked due to landslides | Stricter building codes introduced - but not always enforced |
| Landslides - village of Ghodatabela covered, leading to 250 deaths | Asian Development Bank (ADB) provided US$3 million grant |
| Over 600,000 houses destroyed and over 250,000 damaged | Grants of US$3000 for people to rebuild homes - Many have not re-paid this 5 years later |
| UNESCO World Heritage sites destroyed - Changu Narayan Temple and Dharahara Tower | |
| 8,300 Schools damaged or destroyed | |
| 1,000 health centres destroyed |
Case Study: Impact of Volcanoes
- Name - Mount Merapi
- Location - Java, Indonesia
- Date - 25th October -30th November 2010
- Magnitude - VEI 4
- Plate boundary - Destructive plate boundary where the Indo-Australian plate is subducting below the Eurasian plate
- Type of volcano - Stratovolcano or composite
?Ash fall on village near to Mount Merapi
| Short Term Impacts | Long Term Impacts |
| 353 deaths | Hazard map updated and exclusion zone expanded permanently to 2.5km |
| 577 injuries | 0ver 2,500 residents moved to permanent new homes |
| Pyroclastic flow travelled 3km | Money given to farmers by the government to replace livestock and crops |
| Volcanic ash fell up to 480km away | Improved monitoring |
| 30cm of ash covered nearby villages including Bronggang 15km from the volcano and Yogyakarta | Increased education to inform people of what to do and where to go in the event of another eruption |
| Exclusion zone extended to 20km | Dams built to hold back lahars |
| Roads blocked | Soils will be more fertile due to the minerals contained in the falling ash |
| Food prices increase | |
| 350,000 people evacuated | |
| Schools and airports closed | |
| Lahars | |
| Decrease in tourism income |
Exam Tip
Remember, whether you use the case studies here or ones you have completed in class, in the exam you will be expected to know some facts and figures from case studies. These are place specific details and is what the examiner will be looking for in higher level answers.
轉載自savemyexams

最新發布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









