- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Chemistry: HL復(fù)習(xí)筆記10.2.1 Alkanes - Combustion
Unreactive Alkanes
Strength of C-H bonds
- Alkanes consist of carbon and hydrogen atoms which are bonded together by?single?bonds
- Unless a lot of heat is supplied, it is difficult to break these?strong?C-C and C-H covalent bonds
- This decreases the reactivity of alkanes in chemical reactions
Lack of polarity
- The?electronegativities?of the carbon and hydrogen atoms in alkanes are almost the same
- This means that both atoms share the electrons in the covalent bond almost equally
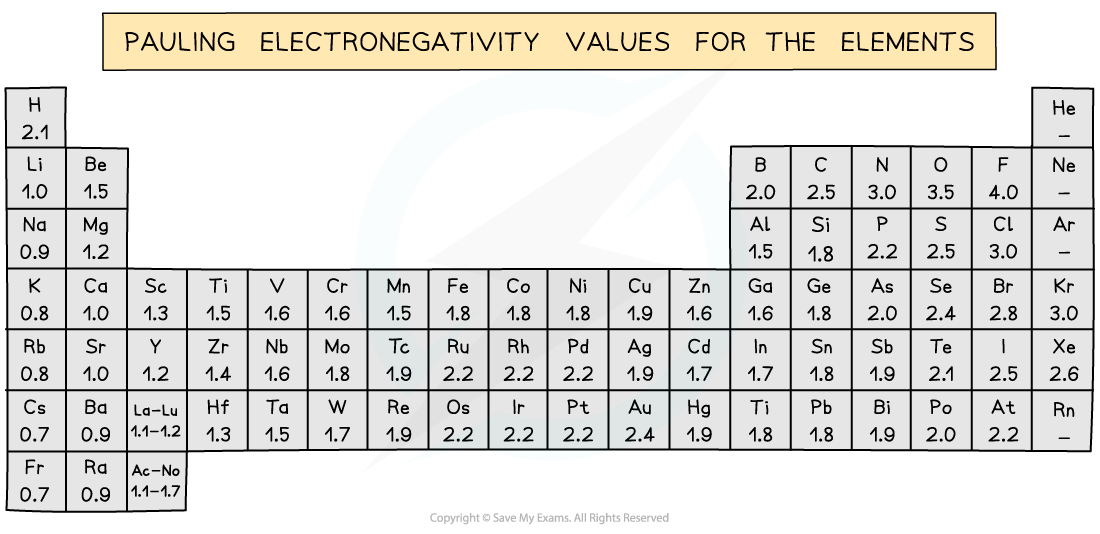
The Pauling Scale shows that the difference in electronegativity between carbon and hydrogen is only 0.4
- As a result of this, alkanes are?nonpolar?molecules and have no partial positive or negative charges (δ+?and δ-?respectively)
- Alkanes therefore do not react with?polar reagents
- They have no electron-deficient areas to attract?nucleophiles
- And also lack electron-rich areas to attract?electrophiles
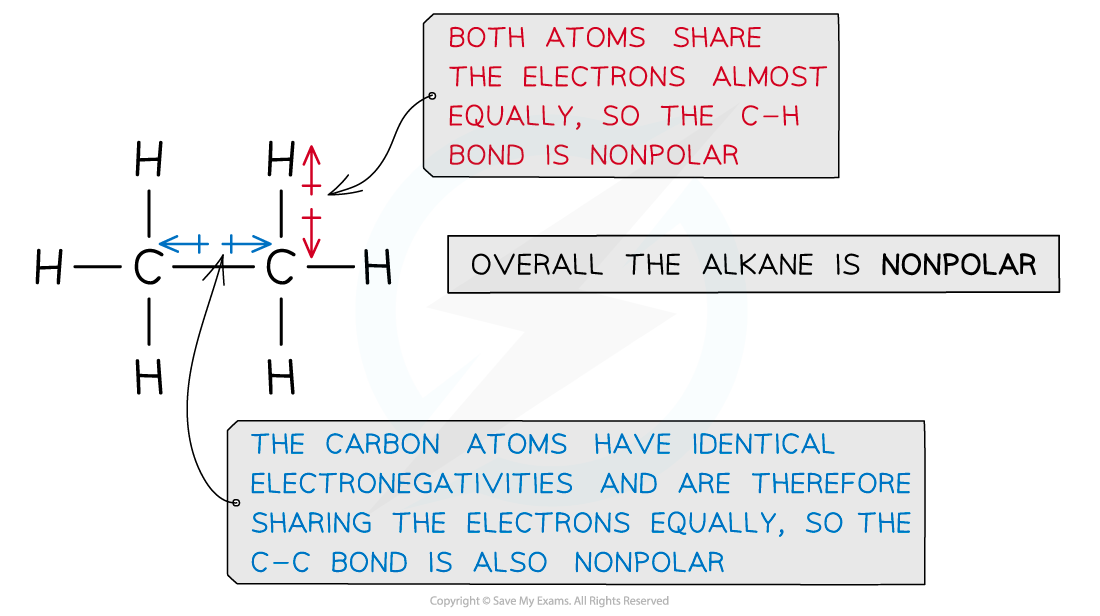
Ethane is an example of an alkane that lacks polarity due to almost similar electronegativities of the carbon and hydrogen atoms
- Due to the unreactivity of alkanes, they only react in combustion reactions and undergo substitution by halogens
Exam Tip
Remember: nucleophiles are negatively charged and are attracted to electron-deficient regions.Electrophiles are positively charged and attracted to electron-rich regions.
Combustion of Alkanes
- Alkanes are?combusted?(burnt) on a large scale for their use as fuels
- They also react in?free-radical substitution?reactions to form more reactive halogenoalkanes
Complete combustion
- When alkanes are burnt in?excess?(plenty of) oxygen,?complete combustion?will take place and all carbon and hydrogen will be oxidised to?carbon dioxide?and?water?respectively
- For example, the complete combustion of octane to carbon dioxide and water
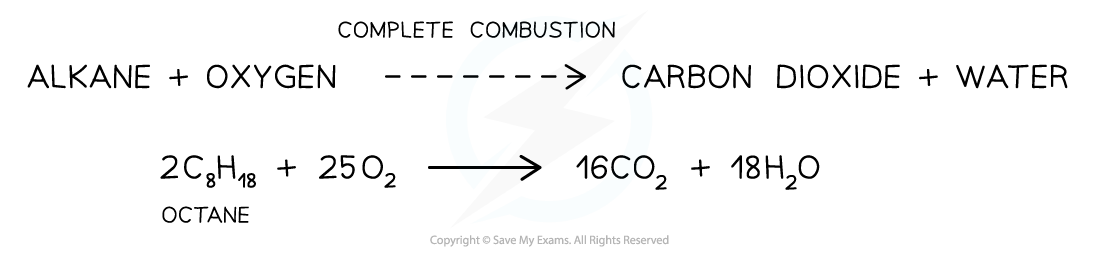
The complete combustion of alkanes
Incomplete combustion
- When alkanes are burnt in only a?limited supply?of oxygen,?incomplete combustion?will take place and not all the carbon is fully oxidised
- Some carbon is only?partially?oxidised to form?carbon monoxide
- For example, the incomplete combustion of octane to form carbon monoxide
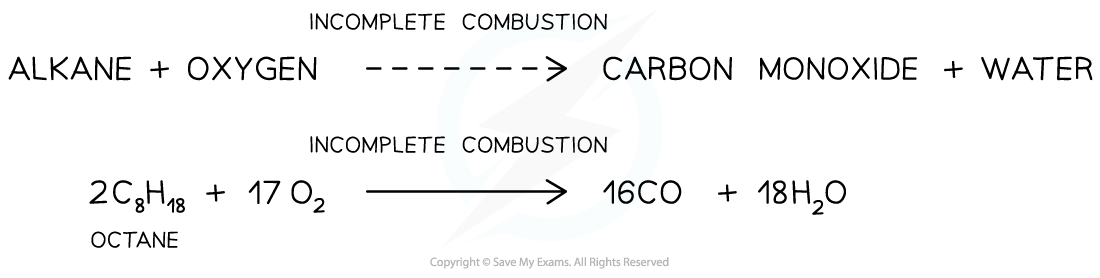
The incomplete combustion of alkanes
- Carbon monoxide is a?toxic?gas as it will bind to haemoglobin in blood which can then no longer bind?oxygen
- As no oxygen can be transported around the body, victims will feel?dizzy, lose consciousness?and if not removed from the carbon monoxide, they can?die
- Carbon monoxide is extremely dangerous as it is?odourless?(it doesn’t smell) and will not be noticed
- Incomplete combustion often takes place inside a?car engine?due to a limited amount of oxygen present
- With a reduced supply of oxygen,?carbon will be produced in the form of soot:

The incomplete combustion of alkanes (2)
Exam Tip
Incomplete combustion of alkanes never produces hydrogen as it is always preferentially oxidised in any available oxygen, rather than carbon
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









