- 翰林提供學(xué)術(shù)活動、國際課程、科研項目一站式留學(xué)背景提升服務(wù)!
- 400 888 0080
IB DP Physics: HL復(fù)習(xí)筆記11.3.2 Dielectric Materials
Dielectric Materials
- Permittivity is the measure of how easy it is to generate an electric field in a certain material
- The relativity permittivity?εr?is sometimes known as the?dielectric constant
- For a given material, it is defined as:
The ratio of the permittivity of a material to the?permittivity of free space
- This can be expressed as:
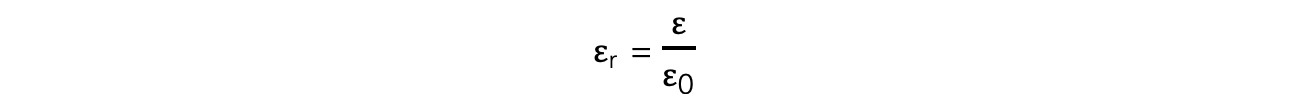
- Where:
- εr?= relative permittivity
- ε?= permittivity of a material (F m-1)
- ε0?= permittivity of free space (F m-1)
- The relative permittivity has?no?units because it is a ratio of two values with the same unit
Worked Example
Calculate the permittivity of a material that has a relative permittivity of 4.5 × 1011. State an appropriate unit for your answer.
Step 1: Write down the relative permittivity equation
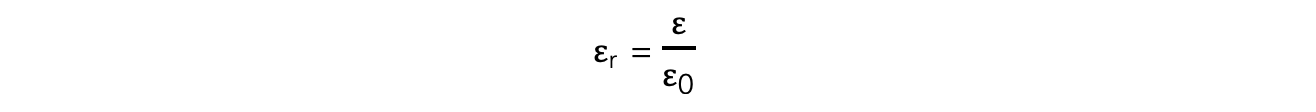
Step 2: Rearrange for permittivity of the material ε
ε = εrε0
Step 3: Substitute in the values
ε = (4.5 × 1011) × (8.85 × 10-12) = 3.9825 = 4 F m-1
Dielectric Material Effects on Capacitance
- A dielectric material separates the two conductive metal plates of a capacitor
- The dielectric itself is an?insulator
- When the polar molecules in a?dielectric?align with the applied electric field from the plates, they each produce their own electric field
- This electric field?opposes?the electric field from the plates
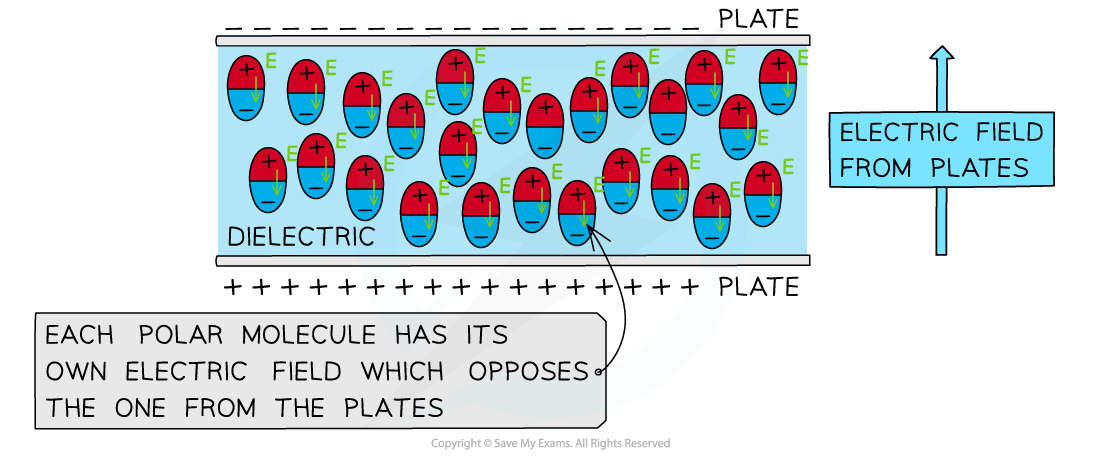
The electric field of the polar molecules opposes that of the electric field produced by the parallel plates
- The?larger?the opposing electric field from the polar molecules in the dielectric, the?larger?the permittivity
- In other words, the permittivity is how well the polar molecules in a dielectric align with an applied electric field
- The opposing electric field?reduces?the?overall?electric field
- For an?isolated?capacitor, this?decreases?the potential difference between the plates
- Therefore, the?charge?remains constant and the?capacitance?of the plates?increases
- For a capacitor attached to a?power supply, the potential difference between the plates is?unchanged?(with a dielectric)
- Therefore, the?charge?on one of the plates?increases?and the?capacitance?of the plates also?increase
- The capacitance of a capacitor can also be written in terms of the relative permittivity:
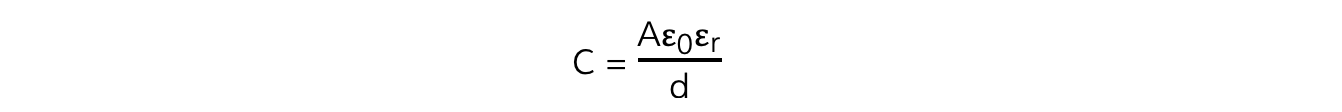
- Where:
- C?=?capacitance?(F)
- A?= cross-sectional area of the plates (m2)
- d?= separation of the plates (m)
- εr?= relative permittivity of the dielectric between the plates
- ε0?=?permittivity of free space?(F m?1)
- When the electrical permittivity of the dielectric is known, a simpler form of this equation can be used:
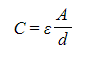
- Where:
- C?= Capacitance (F)
- A?= cross-sectional area of the plates (m2)
- d?= separation of the plates (m)
- ε?= permittivity of the dielectric between the plates (F m?1)
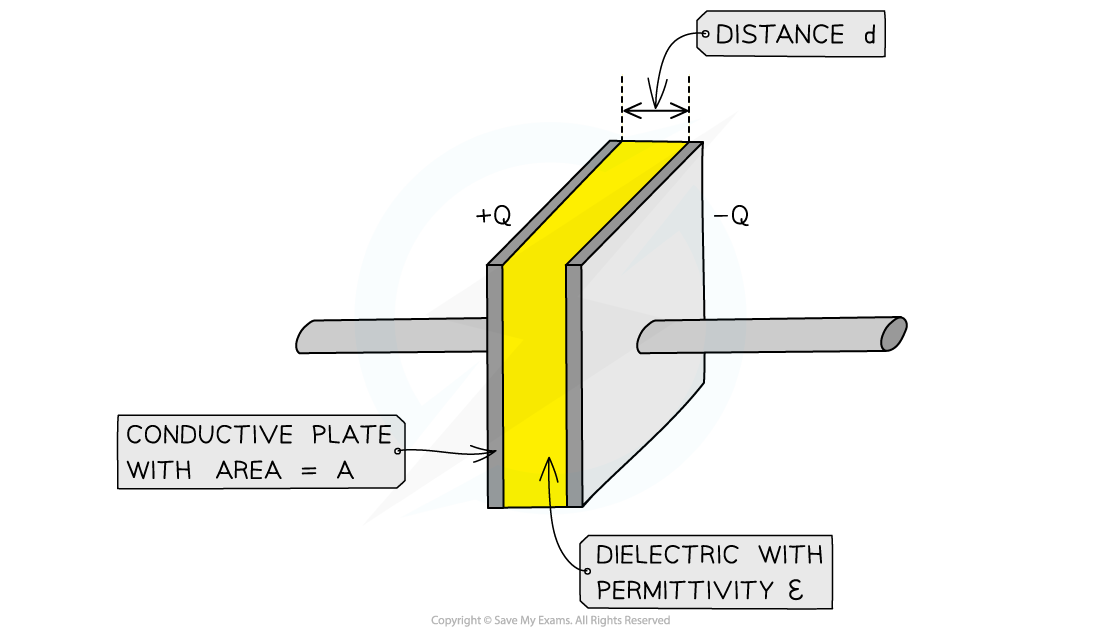
A parallel plate capacitor consists of conductive plates each with area A, a distance d apart and a dielectric ε between them
- Capacitor plates are generally square, therefore if they have a length?L?on all sides then their cross-sectional area is?L2
Worked Example
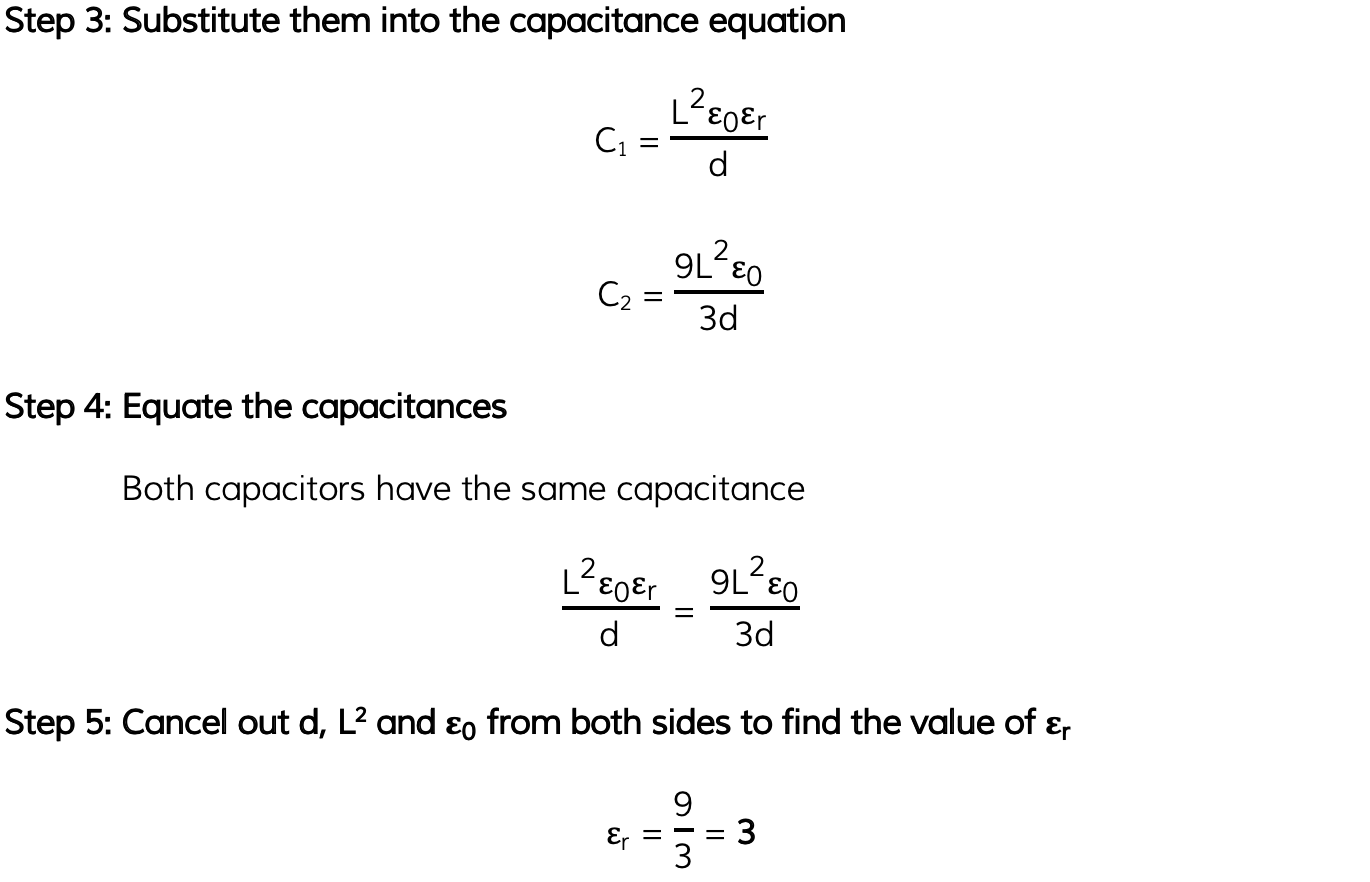
A parallel-plate capacitor has square plates of length?L?separated by distance?d?and is filled with a dielectric. A second capacitor has square plates of length?3L?separated by distance 3d?and has air as its dielectric. Both capacitors have the same capacitance.
Determine the relative permittivity of the dielectric in the first capacitor.

Exam Tip
Remember that?A, the cross-sectional area, is only for?one?of the parallel plates. Don't multiply this by 2 for both the plates for the capacitance equation!
轉(zhuǎn)載自savemyexams

最新發(fā)布
? 2025. All Rights Reserved. 滬ICP備2023009024號-1









